A Science News Aggregator That Covers Stories in the World Of Science And Technology.
Wednesday, March 25, 2009
Rise Of The Robots--The Future Of Artificial Intelligence
From Scientific American:
By 2050 robot "brains" based on computers that execute 100 trillion instructions per second will start rivaling human intelligence
Editor's Note: This article was originally printed in the 2008 Scientific American Special Report on Robots. It is being published on the Web as part of ScientificAmerican.com's In-Depth Report on Robots.
In recent years the mushrooming power, functionality and ubiquity of computers and the Internet have outstripped early forecasts about technology’s rate of advancement and usefulness in everyday life. Alert pundits now foresee a world saturated with powerful computer chips, which will increasingly insinuate themselves into our gadgets, dwellings, apparel and even our bodies.
Read more ....
British Scientists To Create 'Synthetic' Blood
 From The Independent:
From The Independent:Human embryos will be used to make an unlimited supply for infection-free transfusions.
Scientists in Britain plan to become the first in the world to produce unlimited amounts of synthetic human blood from embryonic stem cells for emergency infection-free transfusions.
A major research project is to be announced this week that will culminate in three years with the first transfusions into human volunteers of "synthetic" blood made from the stem cells of spare IVF embryos. It could help to save the lives of anyone from victims of traffic accidents to soldiers on a battlefield by revolutionising the vital blood transfusion services, which have to rely on a network of human donors to provide a constant supply of fresh blood.
Read more ....
Tuesday, March 24, 2009
Mt. Redoubt In Alaska Erupts
Video of the sixth eruption, from the Alaska Volcano observatory webcam system. (h/t to Ron De Haan)
From The Volcanism Blog:
Redoubt-watchers will be aware that the Alaska Volcano Observatory’s Hut webcam went offline during the eruption yesterday, but came back again towards the end of the afternoon. As a result images were captured of the eruptive activity - the sixth explosive event - that took place from 19:41 local time onwards yesterday.
From these webcam images Akira Shirakawa has compiled a video, with synchronized sound, that shows activity between 19:19 and 20:43, available at YouTube. Large-scale ash emission makes everything very dark around 19:50 (at video time 0:24), and a big ash eruption can be clearly seen at 20:01 (video time 0:34).
There is also a page of Hut webcam images and a time-lapse movie here (h/t Chris Rowan, via comment at Eruptions).
Read more ....

Cancer Breakthrough: Tales Of 'Trojan Horse Drug' And 'Miracle Dogs'
 Oscar, who scientists dubbed the "miracle dog," survived an aggressive form of cancer thanks a drug known as NO-Cbl. The drug may lead to a powerful new cancer treatment for humans. (Credit: Crandall B. Huckins)
Oscar, who scientists dubbed the "miracle dog," survived an aggressive form of cancer thanks a drug known as NO-Cbl. The drug may lead to a powerful new cancer treatment for humans. (Credit: Crandall B. Huckins)From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 24, 2009) — Diagnosed with an extremely aggressive form of cancer called anal sac adenocarcinoma, Oscar's future seemed bleak. Bedridden and unresponsive to chemotherapy or radiation, he would be lucky to survive three months. But thanks to an innovative new drug treatment, Oscar's cancer receded and he was walking again within two weeks.
Oscar's recovery was extraordinary enough, but his case was unusual for another reason. Oscar is a Bichon Frise, who scientists reporting in Salt Lake City, Utah at the 237th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society on March 23 call "the Miracle Dog." Joseph A. Bauer, Ph.D., and colleagues described promising results with a drug called nitrosylcobalamin (NO-Cbl) in battling cancer in Oscar and three other canines without any negative side effects. While it gives profound hope to dog owners, NO-Cbl also points to a powerful new cancer treatment for humans — one that infiltrates cancer cells like a biological Trojan horse.
Read more ....
Oldest Sea Creatures Have Been Alive 4,000 Years
 Radiocarbon dating results show deep-sea "corals" with proteinaceous skeletons such as the pictured Gerardia sp. on basalt outcrop, Hawai'ian Islands, are feeding on recently exported young and fresh particulate organic matter and that individual colony longevities are on the order of thousands of years. Credit: NOAA's Hawaii Undersea Research Laboratory (HURL)
Radiocarbon dating results show deep-sea "corals" with proteinaceous skeletons such as the pictured Gerardia sp. on basalt outcrop, Hawai'ian Islands, are feeding on recently exported young and fresh particulate organic matter and that individual colony longevities are on the order of thousands of years. Credit: NOAA's Hawaii Undersea Research Laboratory (HURL)From Live Science:
Deep-sea corals are the oldest living animals with a skeleton in the seas, claims new research that found a 4,265-year-old coral species off the coast of Hawaii.
Deep-sea corals, which are threatened by climate change and pollution like shallow water corals are, grow on seamounts (mountains rising from the seafloor that don't reach the ocean's surface) and continental margins at depths of about 1,000 to 10,000 feet (300 to 3,000 meters).
These corals play host to many other marine organisms, and are hotspots of ocean biodiversity. The largest coral reef system in the world is the Great Barrier Reef off the coast of Queensland, Australia. Big reefs are also found in the Red Sea, along the coast of Mexico and Belize, the Bahamas and the Maldives.
Read more .....
Laser Weapon Design Hits 100-Kilowatt Target
 A Northrop Grumman Space Technology engineer in Redondo Beach, Calif., monitors a solid-state laser, in a photo from January 2007. (Credit: Northrop Grumman)
A Northrop Grumman Space Technology engineer in Redondo Beach, Calif., monitors a solid-state laser, in a photo from January 2007. (Credit: Northrop Grumman)From CNET:
From the week gone by on the directed-energy weapons front: defense contractor Northrop Grumman reported that it got a solid-state laser to fire a beam with a potency of 105.5 kilowatts.
For the ray-gun wing of the military-industrial complex, the 100-kilowatt threshold is a major milestone, marking the entry point to weapons-grade laser weapons. Adding to the appeal is that solid-state lasers are much more compact, and less noxious, than chemical laser systems such as the one in the works for the 747-centric Airborne Laser.
Read more ....
Dogs Show A Fetching Communication Savvy
From Science News:
Border collies know to retrieve toys when owners present replicas or, in some cases, photos of those toys.
Dogs are lousy conversationalists and can’t write worth a lick. But don’t sell the family pooch short when it comes to grasping subtle references in human communication, a new study suggests.
Border collies quickly realize that their owners want them to fetch a toy from another room when shown a full-size or miniature replica of the desired item and given a command to “bring it here,” say biological psychologist Juliane Kaminski of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and her colleagues. Even a photograph of a toy works with some dogs as a signal to fetch that toy from an unseen location, the researchers report in an upcoming issue of Developmental Science.
Read more ....
How (And Why) Athletes Go Broke
 From Sports Illustrated:
From Sports Illustrated:Recession or no recession, many NFL, NBA and Major League Baseball players have a penchant for losing most or all of their money. It doesn't matter how much they make. And the ways they blow it are strikingly similar.
What the hell happened here? Seven floors above the iced-over Dallas North Tollway, Raghib (Rocket) Ismail is revisiting the question. It's December, and Ismail is sitting in the boardroom of Chapwood Investments, a wealth management firm, his white Notre Dame snow hat pulled down to his furrowed brow.
In 1991 Ismail, a junior wide receiver for the Fighting Irish, was the presumptive No. 1 pick in the NFL draft. Instead he signed with the CFL's Toronto Argonauts for a guaranteed $18.2 million over four years, then the richest contract in football history. But today, at a private session on financial planning attended by eight other current or onetime pro athletes, Ismail, 39, indulges in a luxury he didn't enjoy as a young VIP: hindsight.
Read more ....
New Hope For Controversial 'Cold Fusion' Power Source
 An experimental "cold fusion" device produced this pattern of "triple tracks" (shown at right), which scientists say is caused by high-energy nuclear particles resulting from a nuclear reaction. Credit: Pamela Mosier-Boss, Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center (SPAWAR)
An experimental "cold fusion" device produced this pattern of "triple tracks" (shown at right), which scientists say is caused by high-energy nuclear particles resulting from a nuclear reaction. Credit: Pamela Mosier-Boss, Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center (SPAWAR)From Live Science:
If cold fusion can be made to work, it could power the world cheaply on a virtually limitless supply of seawater. But scientists don't even know if it's possible.
Now a new study has produced evidence for the existence of low-energy nuclear reactions (LENR), the new name for the controversial process labeled "cold fusion" two decades ago.
Fusion is the energy source of the sun and other stars. It occurs when atomic nuclei are combined. Today's nuclear plants employ fission, the splitting of nuclei. Scientists have been striving for decades to tap fusion to produce electricity from an abundant fuel called deuterium that can be extracted from seawater. Fusion would not come with the radioactive byproducts of fission.
Read more ....
Curious Pair Of Galaxies: Best Image Ever Of Strange And Chaotic Duo
 This colour composite image of Arp 261 was created from images obtained using the FORS2 instrument on the ESO Very Large Telescope (VLT), at the Paranal Observatory in Chile. Located 2600 m above sea level, in the mountains of the Atacama Desert, the Paranal Observatory enjoys some of the clearest and darkest skies on the whole planet. (Credit: Image courtesy of ESO)
This colour composite image of Arp 261 was created from images obtained using the FORS2 instrument on the ESO Very Large Telescope (VLT), at the Paranal Observatory in Chile. Located 2600 m above sea level, in the mountains of the Atacama Desert, the Paranal Observatory enjoys some of the clearest and darkest skies on the whole planet. (Credit: Image courtesy of ESO)From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 23, 2009) — The ESO Very Large Telescope has taken the best image ever of a strange and chaotic duo of interwoven galaxies. The images also contain some surprises — interlopers both far and near.
Sometimes objects in the sky that appear strange, or different from normal, have a story to tell and prove scientifically very rewarding. This was the idea behind Halton Arp’s catalogue of Peculiar Galaxies that appeared in the 1960s. One of the oddballs listed there is Arp 261, which has now been imaged in more detail than ever before using the FORS2 instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope. The image proves to contain several surprises.
Read more ....
Monday, March 23, 2009
Drink Up: Taking the Salt Out of Seawater
 FREE FROM SALT: Special membranes help desalinize 25 million gallons of water a day at the Tampa Bay Seawater Desalination Plant in Florida. COURTESY OF DOW
FREE FROM SALT: Special membranes help desalinize 25 million gallons of water a day at the Tampa Bay Seawater Desalination Plant in Florida. COURTESY OF DOWFrom Scientific American:
Removing the salt from briny water is becoming more affordable.
Almost three quarters of Earth's surface is covered with water, but most of it is too salty to drink. And the 2.5 percent that is freshwater is locked up either in soil, remote snowpacks and glaciers or in deep aquifers. That leaves less than 1 percent of all freshwater for humans and animals to drink and for farmers to use to raise crops—and that remnant is shrinking as rising global temperatures trigger more droughts. The upshot: it's becoming increasingly difficult to slake the world's thirst as the population grows and water supplies dwindle. Analysts at the investment bank Goldman Sachs estimate that worldwide water use doubles every 20 years.
Read more ....
The Physicists Killed Wall Street
 From Discover Magazine:
From Discover Magazine:A couple of weeks ago there was an interesting opinion piece in the NYTimes about how physicists are the harbingers of doom, and are responsible for the end times. Or, more specifically, it’s because of physicists that the financial markets are in tatters all around us.
The basic idea is that greedy physicists have gone to Wall Street, cooked up all sorts of arcane derivative products, and subsequently unleashed these weapons of mass destruction on the financial markets. This sentiment is best epitomized by a statement from none other than Warren Buffett (perhaps the world’s most successful investor, and certainly the world’s richest): “beware of geeks bearing formulas”
Read more ....
Can Science Reveal The Truth?

From First Science:
In St John's gospel, Jesus Christ tells Pilate that he has come into the world to bear witness to the truth. To which, Pilate famously responds: "What is truth?" - a question that, for me at least, makes Pontius Pilate leap off the page as one of the most human of Biblical characters.
Perhaps the single greatest strength of science is that doesn't have to face up to the meaning of truth: Science's very methodology allows it to sidestep the whole issue of truth. The scientific method is a way of translating our individual responses to the world into something that's collective.
Read more ....
A Machine That Speeds Up Evolution
 Photo: Better bugs: Using a specially designed machine (shown here), scientists can rapidly engineer up to 50 genetic changes in bacteria, dramatically speeding the quest to design bacterial factories capable of efficiently producing drugs, biofuels, and other chemical products. Credit: George Church
Photo: Better bugs: Using a specially designed machine (shown here), scientists can rapidly engineer up to 50 genetic changes in bacteria, dramatically speeding the quest to design bacterial factories capable of efficiently producing drugs, biofuels, and other chemical products. Credit: George ChurchFrom Technology Review:
A genome-wide approach to genetic engineering greatly speeds the manufacture of bacteria for making drugs and biofuels.
Rather than changing the genome letter by letter, as most genetic engineering is done, George Church and his colleagues have developed a new technology that can make 50 changes to a bacterial genome nearly simultaneously--an advance that could be used to greatly speed the creation of bacteria that are better at producing drugs, nutrients, or biofuels.
"What once took months now takes days," says Stephen del Cardayré, vice president of research and development at LS9, a biofuels company based in South San Francisco of which Church is a founder. LS9 soon plans to use the technology--called multiplex-automated genomic engineering, or MAGE--to accelerate development of bacterial cells that can produce low-cost renewable fuels and chemicals.
Read more ....
Physics In The Oil Sands Of Alberta
From Physics Today:
Alberta’s petroleum reserves are comparable to Saudi Arabia’s, but accessing that oil poses challenges in the physics of fluids and particulates.
The recent spike in the price of oil to over US$140 per barrel focused worldwide attention on the need for more diverse supplies of fuel from unconventional sources and renewable resources. The oil sands of Alberta, the largest source of unconventional fuel for North America, are also the largest petroleum deposit on Earth. Sometimes called tar sands, they contain an estimated 2.5 trillion barrels of crude oil over an area of more than 140 000 square kilometers, but that oil, called bitumen, is too viscous to be extracted by conventional drilling. Large oil-sands deposits also exist in Venezuela, and smaller ones are found in Utah, western Africa, and Russia, but production from the Canadian deposits is the largest.
Read more ....
Alaska's Mt. Redoubt Volcano Is Erupting; Large Explosions Recorded
 Alaska's Mt. Redoubt Volcano, which had been in a tempestuous mood for two months,
Alaska's Mt. Redoubt Volcano, which had been in a tempestuous mood for two months,began erupting early this morning.
From the L.A. Times:
Alaska's Mt. Redoubt Volcano, which had been in a tempestuous mood for two months, began erupting early this morning.
The Alaska Volcano Observatory recorded four large explosions at Redoubt volcano in the predawn darkness Monday, and at 7 a.m. the website anounced, "Another large explosion has just occurred."
The height of the eruption cloud is estimated to be 50,000 feet above sea level, but it remains unclear what direction the enormous plume will travel.
Two calls to the AVO/U.S. Geological Survey operations center went unanswered.
Read more .....
More News On Alaska's Mt. Redoubt Volcano
Mount Redoubt Volcano Erupts Five Times, So Far -- Live Science
Alaska's Mount Redoubt erupts after weeks of waiting -- McClatchy
Alaska's Mount Redoubt has 5th eruption -- UPI
Alaska's Mount Redoubt erupts -- Examiner
Mount Redoubt blows its top -- CBS 12
Carbon Nanotube Muscles Strong As Diamond, Flexible As Rubber

From Wired News:
For the next installment of the Terminator franchise, Hollywood might skip the polymimetic liquid alloys — they're so 2003 — and turn to the laboratory of Ray Baughman, who has created a next-generation muscle from carbon nanotubes.
Baughman and his colleagues have produced a formulation that's stronger than steel, as light as air and more flexible than rubber — a truly 21st century muscle. It could be used to make artificial limbs, "smart" skins, shape-changing structures, ultra-strong robots and — in the immediate future — highly-efficient solar cells.
Read more ....
Language Of Music Really Is Universal, Study Finds
 A saxophonist. Native African people who have never even listened to the radio before can nonetheless pick up on happy, sad, and fearful emotions in Western music. (Credit: iStockphoto/Richard Clarke)
A saxophonist. Native African people who have never even listened to the radio before can nonetheless pick up on happy, sad, and fearful emotions in Western music. (Credit: iStockphoto/Richard Clarke)From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 20, 2009) — Native African people who have never even listened to the radio before can nonetheless pick up on happy, sad, and fearful emotions in Western music, according to a new report published online on March 19th in Current Biology. The result shows that the expression of those three basic emotions in music can be universally recognized, the researchers said.
"These findings could explain why Western music has been so successful in global music distribution, even in music cultures that do not as strongly emphasize the role of emotional expression in their music," said Thomas Fritz of the Max-Planck-Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences.
Read more ....
Sunday, March 22, 2009
Living Model Of Basic Units Of Human Brain Created
 An isolated astrocyte shown with confocal microscopy. (Credit: Image created by Nathan S. Ivey at TNPRC / courtesy of Wikipedia)
An isolated astrocyte shown with confocal microscopy. (Credit: Image created by Nathan S. Ivey at TNPRC / courtesy of Wikipedia)From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 22, 2009) — Researchers in the School of Life & Health Sciences at Aston University in Birmingham, UK are developing a novel new way to model how the human brain works by creating a living representation of the brain.
They are using cells originally from a tumour which have been ‘reprogrammed’ to stop multiplying. Using the same natural molecule the body does to stimulate cellular development, the cells are turned into a co-culture of nerve cells and astrocytes - the most basic units of the human brain.
Read more ....
Star Explodes, And So Might Theory
 This artist's illustration provided by NASA shows what the brightest supernova ever recorded, known as SN 2006gy, may have looked like when it exploded. Photo: AP/NASA
This artist's illustration provided by NASA shows what the brightest supernova ever recorded, known as SN 2006gy, may have looked like when it exploded. Photo: AP/NASAFrom Live Science:
A massive star a million times brighter than our sun exploded way too early in its life, suggesting scientists don't understand stellar evolution as well as they thought.
"This might mean that we are fundamentally wrong about the evolution of massive stars, and that theories need revising," said Avishay Gal-Yam of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel.
According to theory, the doomed star, about 100 times our sun's mass, was not mature enough to have evolved a massive iron core of nuclear fusion ash, considered a prerequisite for a core implosion that triggers the sort of supernova blast that was seen.
Read more ....
'Star Wars' Scientists Create Laser Gun To Kill Mosquitoes
 From CNN:
From CNN:LONDON, England -- Scientists in the U.S. are developing a laser gun that could kill millions of mosquitoes in minutes.
The laser, which has been dubbed a "weapon of mosquito destruction" fires at mosquitoes once it detects the audio frequency created by the beating of its wings.
The laser beam then destroys the mosquito, burning it on the spot.
Developed by some of the astrophysicists involved in what was known as the "Star Wars" anti-missile programs during the Cold War, the project is meant to prevent the spread of malaria.
Lead scientist on the project, Dr. Jordin Kare, told CNN that the laser would be able to sweep an area and "toast millions of mosquitoes in a few minutes."
Read more ....
The New King Coal: The Unlikely Comeback Of The Mining Industry
 The Dosco machine bores access routes to the coal face at Daw Mill, the most productive colliery in British history. Last year it produced 3.17 million tons of coal
The Dosco machine bores access routes to the coal face at Daw Mill, the most productive colliery in British history. Last year it produced 3.17 million tons of coalFrom The Daily Mail:
Oil is running out, Russia controls most of Europe's gas and our weary nuclear generators are on their last legs. So what will power Britain in the future?James Delingpole reports on the unlikely comeback of coal.
'Some people can't handle it,' says the pit manager, raising his voice above the trundle of the battery-powered train and nodding to the walls of the dimly lit passageways taking us to the coal face in the Warwickshire Thick seam at Daw Mill colliery, near Coventry.
'They'll suddenly freeze and refuse to go any further.'
'What - here?' I ask, secretly thinking how pathetic that would be. So far on our descent the tunnels have been surprisingly broad and high. There's plenty of air and lots of joking, confident miners to keep spirits high.
'No. Further on. Where the tunnel starts to narrow.'
'How narrow?'
'You'll see.'
Read more ....
Could A Helmet Have Saved Natasha Richardson?
From Time Magazine:
There is still more speculation than information surrounding actress Natasha Richardson's fateful ski accident. Part of the confusion is the very nature of the accident — an improbable injury, little more than a head bump on a bunny slope, that has felled an otherwise healthy 45-year-old woman. It has also left onlookers wondering not just what happened to Richardson, but whether a helmet could have prevented it.
The details of Richardson's accident are sketchy, but what is known sounded benign — at first. She was taking a lesson on a beginner slope at the Mont Tremblant ski resort north of Montreal, with an instructor but without a helmet. She fell at the end of the lesson and struck her head, but was alert and conversational afterward and did not complain of any ill effects. An hour later, in her hotel room, she developed a severe headache. The next day, she was flown to Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City in critical condition, where she died on Wednesday.
Read more ....
Knowing Blends Science Fact With Fiction (Beware: Spoilers!)

From Popular Mechanics:
In Knowing, numbers predict every major disaster for 50 years—and the upcoming end of the world. But just how much can scientists predict? PM talks to MIT physicist Dr. Edward Farhi to find out. Beware: Spoilers ahead!
In Knowing, Nicholas Cage plays John Kessler, an MIT astrophysicist who believes that the universe's course is caused by random events and circumstances with no grand plan—until a mysterious numerical code, unearthed from a time capsule buried for half a century, correctly predicts every major disaster of the last 50 years. The catch? It also predicts the upcoming end of the world. Knowing's plot is part real astrophysics and part mysticism; PM's Digital Hollywood got to the bottom of what is fact—and what's science fiction.
Read more ....
How Pterosaurs Could Improve Robot Planes
 Hop, Skip, and Away: Paleontologist Michael Habib theorizes that pterosaurs, which lived between 250 million and 65 million years ago, used their legs and wing “knuckles”—not just their hind legs, as previously believed—to leapfrog into flight. Kevin Hand
Hop, Skip, and Away: Paleontologist Michael Habib theorizes that pterosaurs, which lived between 250 million and 65 million years ago, used their legs and wing “knuckles”—not just their hind legs, as previously believed—to leapfrog into flight. Kevin Hand Flight School -- Popsci.com
A new take on pterosaurs could improve robot planes
If it looks like a duck and flies like a duck, it must take off like a duck. Paleontologists long speculated that this was the case for pterosaurs, but new research shows that the prehistoric winged lizards employed a smarter launch strategy, using all four limbs to hop, skip, and jump their way into flight, instead of pushing off with two legs and flapping their wings as most birds do.
Read more ....
Earth's Future: Scary Ozone Scenario Thwarted
 Simulations of global ozone concentration show the real-world ozone layer (left) versus a "world avoided," in which CFCs had never been banned. Reds depict high concentration; dark blues show low concentrations. Note the seasonal pulse of ozone over the poles, how it declines to holes (blue), then becomes global depletion by the 2050s. 2009 shown here. Credit: NASA Goddard's Scientific Visualization Studio
Simulations of global ozone concentration show the real-world ozone layer (left) versus a "world avoided," in which CFCs had never been banned. Reds depict high concentration; dark blues show low concentrations. Note the seasonal pulse of ozone over the poles, how it declines to holes (blue), then becomes global depletion by the 2050s. 2009 shown here. Credit: NASA Goddard's Scientific Visualization StudioFrom Live Science:
If 193 nations hadn’t agreed in 1989 to ban the chemicals that eat up the Earth’s protective ozone layer, the world would have been a much different place later this century, with nearly two-thirds of the ozone layer gone and the ozone hole a permanent fixture over Antarctica, a new simulation shows.
Sunburns would occur in a matter of minutes and skin cancer-causing radiation would soar.
Ozone is the Earth's natural sunscreen, absorbing and blocking most of the incoming ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and protecting life from the DNA-damaging rays.
The gas is naturally created and replenished by a photochemical reaction in the upper atmosphere where UV rays break oxygen molecules (O2) into individual atoms that then recombine into three-part molecules of ozone (O3).
Read more ....
Saturday, March 21, 2009
First 'Rule' Of Evolution Suggests That Life Is Destined To Become More Complex
 Spiny lobster. In complex crustaceans, such as shrimps and lobsters, almost every segment is different, bearing antennae, jaws, claws, walking legs, paddles and gills. (Credit: iStockphoto/Tammy Peluso)
Spiny lobster. In complex crustaceans, such as shrimps and lobsters, almost every segment is different, bearing antennae, jaws, claws, walking legs, paddles and gills. (Credit: iStockphoto/Tammy Peluso)From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 18, 2008) — Researchers have found evidence which suggests that evolution drives animals to become increasingly more complex.
Looking back through the last 550 million years of the fossil catalogue to the present day, the team investigated the different evolutionary branches of the crustacean family tree.
They were seeking examples along the tree where animals evolved that were simpler than their ancestors.
Instead they found organisms with increasingly more complex structures and features, suggesting that there is some mechanism driving change in this direction.
Read more ....
Robot Octopus Will Go Where No Sub Has Gone Before
From New Scientist:
INVEST €10 million in a robotic octopus and you will be able to search the seabed with the same dexterity as the real eight-legged cephalopod. At least that's the plan, say those who are attempting to build a robot with arms that work in the same way that octopuses tentacles do. Having no solid skeleton, it will be the world's first entirely soft robot.
The trouble with today's remote-controlled subs, says Cecilia Laschi of the Italian Institute of Technology in Genoa, is that their large hulls and clunky robot arms cannot reach into the nooks and crannies of coral reefs or the rock formations on ocean floors. That means they are unable to photograph objects in these places or pick up samples for analysis. And that's a major drawback for oceanographers hunting for signs of climate change in the oceans and on coral reefs.
Read more ....
Another Space Walk At The Space Station
 In this image from NASA TV, international crew members, from left, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata, Russian cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, American commander Lee Archambault and American astronaut Sandy Magnus participate in an interview while orbiting Earth, Friday, March 20, 2009. (AP Photo/NASA TV)
In this image from NASA TV, international crew members, from left, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata, Russian cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, American commander Lee Archambault and American astronaut Sandy Magnus participate in an interview while orbiting Earth, Friday, March 20, 2009. (AP Photo/NASA TV)Astronauts Go On 2nd Spacewalk At Space Station -- Yahoo News/AP
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Astronauts took another spacewalk at the international space station Saturday, this time to lighten the workload for future crews.
As soon as they floated outside, Steven Swanson and Joseph Acaba made their way all the way to the end of the space station's power-grid framework. They loosened bolts holding down batteries that will be replaced on the next shuttle visit in June, and deployed an equipment storage platform.
Read more ....
Africans Came With Columbus To New World
 Skeletons that may represent the remains of crew members from Columbus' second excursion to the New World in 1493-94 were exhumed in 1990. The burials were a part of La Isabela on the island of Hispaniola, now a part of the Dominican Republic and that was the first European settlement in the New World. Credit: Fernando Luna Calderon, provided courtesy of T. Douglas Price
Skeletons that may represent the remains of crew members from Columbus' second excursion to the New World in 1493-94 were exhumed in 1990. The burials were a part of La Isabela on the island of Hispaniola, now a part of the Dominican Republic and that was the first European settlement in the New World. Credit: Fernando Luna Calderon, provided courtesy of T. Douglas PriceFrom Live Science:
Teeth from exhumed skeletons of crew members Christopher Columbus left on the island of Hispaniola more than 500 years ago reveal the presence of at least one African in the New World as a contemporary of the explorer, it was announced.
A team of researchers is extracting the chemical details of life history from the remains found at shallow graves at the site of La Isabela, the first European town in America, said T. Douglas Price, a University of Wisconsin-Madison professor of anthropology and leader of the team conducting an analysis of the tooth enamel of three individuals from a larger group excavated almost 20 years ago there.
Read more ....
Finding Twin Earths Is Harder Than Thought
 This artist's conception shows a hypothetical twin Earth orbiting a Sun-like star. A new study shows that characterizing a distant Earth's atmosphere will be difficult, even using next-generation technology like the James Webb Space Telescope. If an Earth-like world is nearby, though, then by adding observations of a number of transits, astronomers should be able to detect biomarkers like methane or ozone. (Credit: David A. Aguilar (CfA))
This artist's conception shows a hypothetical twin Earth orbiting a Sun-like star. A new study shows that characterizing a distant Earth's atmosphere will be difficult, even using next-generation technology like the James Webb Space Telescope. If an Earth-like world is nearby, though, then by adding observations of a number of transits, astronomers should be able to detect biomarkers like methane or ozone. (Credit: David A. Aguilar (CfA))From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 21, 2009) — Does a twin Earth exist somewhere in our galaxy? Astronomers are getting closer and closer to finding an Earth-sized planet in an Earth-like orbit. NASA's Kepler spacecraft just launched to find such worlds. Once the search succeeds, the next questions driving research will be: Is that planet habitable? Does it have an Earth-like atmosphere? Answering those questions will not be easy.
Due to its large mirror and location in outer space, the James Webb Space Telescope (scheduled for launch in 2013) will offer astronomers the first real possibility of finding those answers. In a new study, Lisa Kaltenegger (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) and Wesley Traub (Jet Propulsion Laboratory) examined the ability of JWST to characterize the atmospheres of hypothetical Earth-like planets during a transit, when part of the light of the star gets filtered through the planet's atmosphere. They found that JWST would be able to detect certain gases called biomarkers, such as ozone and methane, only for the closest Earth-size worlds.
Read more ....
Microsoft Launches New Version Of Internet Explorer

From The Daily Mail:
Microsoft has released its latest version of Internet Explorer, which is available free to download.
Internet Explorer 8 is claimed to be a faster, more secure and innovative version of the world's most popular browser.
Steve Ballmer, the chief executive officer of Microsoft, said: ‘With Internet Explorer 8, we are delivering a browser that gets people to the information they need, fast, and provides protection that no other browser can match.’
Read more .....
Strange Particle Created; May Rewrite How Matter's Made
 A particle detector as big as a three-story house records the "debris" emerging from high-energy proton-antiproton collisions in the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. Data from such detectors revealed an unexpected new subatomic particle that may break all known rules governing how matter is created, scientists said in March 2009. Image courtesy Fermilab
A particle detector as big as a three-story house records the "debris" emerging from high-energy proton-antiproton collisions in the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. Data from such detectors revealed an unexpected new subatomic particle that may break all known rules governing how matter is created, scientists said in March 2009. Image courtesy FermilabFrom National Geographic:
An unexpected new subatomic particle has been discovered in Illinois's Fermilab atom smasher, scientists announced this week.
The new particle may break all known rules for creating matter, say the researchers who created the oddity.
Y(4140)—as the new particle has been dubbed—couldn't have formed through either of the two known models for matter creation. Researchers aren't even sure what Y(4140) is made of.
It's long been accepted that six different "flavors" of particles called quarks combine to form larger subatomic particles.
In one method, a quark pairs with one of its opposites, an antiquark, to create a type of matter called a meson. In the second method, three quarks gather to form baryons, such as protons and neutrons.
Read more ....
Romeo And Juliet's Balcony Opens For Weddings
 Well-Worn Juliet Statue
Well-Worn Juliet StatueThe House of Juliet is the 13th century family home of the Cappello family who, according to legend, were the Capulets of Shakespeare's "Romeo and Juliet." The house will soon be used as a venue for weddings. This is the statue of Juliet in the courtyard of the house. The current tradition for couples is to stroke the right breast of the languid bronze statue and then leave love notes on the house's walls. Rossella Lorenzi
From Discover:
March 20, 2009 -- The House of Juliet, with the legendary balcony where Juliet Capulet is said to have pined for Romeo, will soon be used as a venue for weddings, city officials in Verona have announced.
The 13th century family home of the Cappello family who, according to legend, were the Capulets of Shakespeare's tragic play, has been always a place of pilgrimage for lovers from all over the world.
The tradition for couples is to first stroke the right breast of the languid bronze statue of Juliet in the courtyard -- the gesture is believed to bring good luck -- then leave love notes on the house's walls and Gothic wooden doors.
Read more ....
Friday, March 20, 2009
Pink Elephant Is Caught On Camera
From The BBC:
A pink baby elephant has been caught on camera in Botswana.
A wildlife cameraman took pictures of the calf when he spotted it among a herd of about 80 elephants in the Okavango Delta.
Experts believe it is probably an albino, which is an extremely rare phenomenon in African elephants.
They are unsure of its chances of long-term survival - the blazing African sunlight may cause blindness and skin problems for the calf.
Mike Holding, who spotted the baby while filming for a BBC wildlife programme, said: "We only saw it for a couple of minutes as the herd crossed the river.
Read more ....
Go Play Outside To Recharge Yourself
Interviewees: John Jonides and Marc Berman, University of Michigan
Produced by Jack Penland– Edited by James Eagan
Copyright © ScienCentral, Inc
From ScienCentral:
Feeling like you’re suffering from brain drain and you can’t concentrate? Psychologists have now found out that taking some time to interact with nature, even in cold weather, can make you a bit smarter.
Mother Knows Best
Are you feeling the strain of work? Have you lost focus and is your mind feeling about as sharp as the wooden rulers you had in elementary school? Scientists have some advice for you. Advice, it turns out, that your mother already told you a long time ago: Go play outside.
But, it turns out mother was only partly right. John Jonides, University of Michigan professor of psychology and neuroscience, and graduate student Marc Berman have one big condition to that advice: A walk in nature sharpens the mind, but a walk in the city does not.
Read more ....
Two Dying Red Supergiant Stars Produced Supernovae
 The Crab nebula is the result of a type II supernova explosion observed by Chinese astronomers in 1054. The nebula consists of the outer parts of a red supergiant that exploded after having burned all its fuel. The nebula is still expanding into the surrounding interstellar medium with velocities of several thousand kilometers per second. In the middle of the nebula there is a neutron star, which is the collapsed central, dead core of the exploded star. (Credit: Hubble Space Telescope)
The Crab nebula is the result of a type II supernova explosion observed by Chinese astronomers in 1054. The nebula consists of the outer parts of a red supergiant that exploded after having burned all its fuel. The nebula is still expanding into the surrounding interstellar medium with velocities of several thousand kilometers per second. In the middle of the nebula there is a neutron star, which is the collapsed central, dead core of the exploded star. (Credit: Hubble Space Telescope)From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 20, 2009) — Where do supernovae come from? Astronomers have long believed they were exploding stars, but by analysing a series of images, researchers from the Dark Cosmology Centre at the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen and from Queens University, Belfast have proven that two dying red supergiant stars produced supernovae. The results are published in the journal Science.
A star is a large ball of hot gas and in its incredibly hot interior hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, which subsequently forms carbon, other heavier elements and finally iron. When all the atoms in the centre have turned to iron the fuel is depleted and the star dies. When very large and massive stars, that are at least about eight times as massive as our sun, die, they explode as supernovae.
Read more ....
More People In Love Than Previously Thought

From Live Science:
Romeo and Juliet would approve: A new study found that romantic love can stand the test of time.
Though it is widely held that romance and sex must ultimately yield to friendly companionship over time, new research found that's not the case. Instead about 13 percent of people reported high levels of romance in their long-term relationships, in a new study published in the March issue of the journal Review of General Psychology.
Researchers analyzed data from surveys of more than 6,000 people, including some in newly-formed pairs and many in marriages of more than 20 years. The scientists found that a surprisingly high number of people were still very much in love with their long-term partners, though the researchers drew a distinction between romantic love, which can endure, and passionate or obsessive love, which often fades after the beginning of a relationship.
Read more ....
Liquid Saltwater Is Likely Present On Mars, New Analysis Shows
 Droplets on a leg of the Mars Phoenix lander are seen to darken and coalesce. Nilton Renno, a professor in the Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic and Space Sciences says this is evidence that they are made of liquid water. (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/Max Planck Institute)
Droplets on a leg of the Mars Phoenix lander are seen to darken and coalesce. Nilton Renno, a professor in the Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic and Space Sciences says this is evidence that they are made of liquid water. (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/Max Planck Institute)From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 20, 2009) — Salty, liquid water has been detected on a leg of the Mars Phoenix Lander and therefore could be present at other locations on the planet, according to analysis by a group of mission scientists led by a University of Michigan professor. This is the first time liquid water has been detected and photographed outside the Earth.
"A large number of independent physical and thermodynamical evidence shows that saline water may actually be common on Mars," said Nilton Renno, a professor in the U-M Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic and Space Sciences and a co-investigator on the Phoenix mission.
Read more ....
The Quest To Make Hydrogen The Fuel Of The Future
 The world's first hydrogen fuel station in Reykjavik, Iceland, April 2003.
The world's first hydrogen fuel station in Reykjavik, Iceland, April 2003.Photo supplied by about.com
From NOVA:
Australia and many other countries around the world are preparing for hydrogen to take over from fossil fuels such as oil and natural gas, and move to what's being called the 'hydrogen economy'. But there are some big hurdles to overcome before it can happen.
You may not realise it, but scientists, the energy industry, governments and climate change experts around the world have joined forces and are on a global quest - and a race against time. Their goal is to find an economical, practical and safe form of energy to replace our reliance on fossil fuels.
Hydrogen, the most abundant element in the Universe, is one potential candidate. Many regard it as the ultimate 'clean, green' fuel because when it burns in oxygen, only heat and water are created.
Read more ....
If Galaxies Are All Moving Apart, How Can They Collide?
 This Hubble Space Telescope image shows a collision between two spiral galaxies, NGC 6050 and IC 1179, in the Hercules constellation. NASA, ESA and HUBBLE HERITAGE
This Hubble Space Telescope image shows a collision between two spiral galaxies, NGC 6050 and IC 1179, in the Hercules constellation. NASA, ESA and HUBBLE HERITAGEFrom Scientific American:
Cosmologist Tamara Davis, a research fellow at the University of Queensland in Australia and an associate of the Dark Cosmology Center in Denmark, brings together an answer:
The dynamics of the universe are governed by competing forces whose influence varies with scale, so local forces can override universal forces in discrete regions. On scales larger than galaxy clusters, all galaxies are indeed moving apart at an ever increasing rate. The mutual gravitational attraction between two galaxies at that distance is too small to have a significant effect, so the galaxies more or less follow the general flow of the expansion. But it is a different story in a galaxy's local neighborhood. There the gravitational attraction can be very significant and the interactions much more exciting.
Read more ....
Schools Of Robofish To Sniff Out Pollution In The Thames
 Green robofish: The pollutant-seeking robots will be based on this model at the London Aquarium, with sensors to detect contaminants and GPS navigation
Green robofish: The pollutant-seeking robots will be based on this model at the London Aquarium, with sensors to detect contaminants and GPS navigationFrom The Daily Mail:
Schools of robotic fish could be sent into the Thames to produce a 3D pollution map of the river.
Researchers at the University of Essex in Colchester are working on the robofish as part of a £2.5million EU-funded project to find new ways of monitoring water waste.
Each fish will be about 50cm long, 15cm high and 12cm wide. They will be packed with pollution sensors that can electronically 'sniff' harmful chemicals in the water.
Read more ....
Thursday, March 19, 2009
Chris Anderson: Web Creating Free Economy
 From Times Online:
From Times Online:Digital technology is offering consumers better deals and reshaping economic theory, says the author of The Long Tail
The "free economy", where businesses give away their products to make money, is spreading fast thanks to the recession and the increasing reach of digital technology, according to the author Chris Anderson.
Mr Anderson, whose acclaimed book The Long Tail is about how the digital revolution allows businesses to profit from selling small quantities of relatively unpopular items, said that consumers with less in their pockets were looking for bargains, making the free business strategy even more attractive.
Read more ....
Genesis For Exploding Stars Confirmed
 The Crab nebula is the result of a type II supernova explosion observed by Chinese astronomers in 1054. The nebula consists of the outer parts of a red supergiant that exploded after having burned all its fuel. Credit: Hubble Space Telescope
The Crab nebula is the result of a type II supernova explosion observed by Chinese astronomers in 1054. The nebula consists of the outer parts of a red supergiant that exploded after having burned all its fuel. Credit: Hubble Space TelescopeFrom Live Science:
Telescope images have confirmed something astronomers have long suspected, that red supergiant stars are the stars that explode in so-called type II supernovas.
Type II supernovas are the impressive cosmic explosions that result from the internal collapse of a massive star. (For this reason, they are also known as core-collapse supernovas.)
On average, a supernova will occur about once every 50 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way. But scientists don't know when these stellar powder kegs will blow, so identifying the star that birthed them, called the progenitor star, can be tricky.
Read more ....
Tongan Inspection Team Heads To Undersea Volcano
From Yahoo News/AP:
NUKU'ALOFA, Tonga – Scientists sailed Thursday to inspect an undersea volcano that has been erupting for days near Tonga — shooting smoke, steam and ash thousands of feet (meters) into the sky above the South Pacific ocean.
Authorities said Thursday the eruption does not pose any danger to islanders at this stage, and there have been no reports of fish or other animals being affected.
Spectacular columns are spewing out of the sea about 6 miles (10 kilometers) from the southwest coast off the main island of Tongatapu — an area where up to 36 undersea volcanoes are clustered, geologists said.
Read more ....
More News On The Tonga Volcano
Tonga volcano spews spectacular plume into South Pacific sky -- Scientific American
Underwater volcano erupts off Tonga -- BBC
Tongan Eruption, Quake, Tsunami Alert -- New York Times
Underwater volcano sends huge columns of ash into Pacific sky -- Times Online
World Faces 'Perfect Storm' Of Problems By 2030, Chief Scientist To Warn
 Food and water shortages as a result of climate change and growing populations are likely to trigger mass migration and unrest. Photograph: AFP/Getty
Food and water shortages as a result of climate change and growing populations are likely to trigger mass migration and unrest. Photograph: AFP/GettyFrom The Guardian:
Food, water and energy shortages will unleash public unrest and international conflict, Professor John Beddington will tell a conference tomorrow.
A "perfect storm" of food shortages, scarce water and insufficient energy resources threaten to unleash public unrest, cross-border conflicts and mass migration as people flee from the worst-affected regions, the UK government's chief scientist will warn tomorrow.
In a major speech to environmental groups and politicians, Professor John Beddington, who took up the position of chief scientific adviser last year, will say that the world is heading for major upheavals which are due to come to a head in 2030.
Read more ....
Astronauts Successfully Install Solar Wings
 This video still image released by NASA TV, shows Space Shuttle Discovery crew member Steven Swanson, right, being helped with his space suit by international space station commander Lee Archambault before a spacewalk Thursday, March 19, 2009. The spacewalk will be the first of three planned for Discovery's space station visit. (AP Photo/NASA TV)
This video still image released by NASA TV, shows Space Shuttle Discovery crew member Steven Swanson, right, being helped with his space suit by international space station commander Lee Archambault before a spacewalk Thursday, March 19, 2009. The spacewalk will be the first of three planned for Discovery's space station visit. (AP Photo/NASA TV)From Yahoo News/AP:
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Spacewalking astronauts installed the last set of solar wings at the international space station Thursday, accomplishing the top job of shuttle Discovery's mission.
Steven Swanson and Richard Arnold II struggled with some cable connections, but managed to hook everything up.
"It wasn't quite as smooth as we had hoped, but those guys did a great job," astronaut Joseph Acaba told Mission Control.
The next milestone will be Friday, when the folded-up solar wings are unfurled.
Manpower was needed inside and out to attach the $300 million segment to the space station. Swanson and Arnold helped their colleagues inside the shuttle-space station complex cautiously move the 31,000-pound, 45-foot-long girder into position with a robotic arm.
Read more ....
20 Things You Didn't Know About... Time
 From Discover Magazine:
From Discover Magazine:1 “Time is an illusion. Lunchtime doubly so,” joked Douglas Adams in The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy. Scientists aren’t laughing, though. Some speculative new physics theories suggest that time emerges from a more fundamental—and timeless—reality.
2 Try explaining that when you get to work late. The average U.S. city commuter loses 38 hours a year to traffic delays.
3 Wonder why you have to set your clock ahead in March? Daylight Saving Time began as a joke by Benjamin Franklin, who proposed waking people earlier on bright summer mornings so they might work more during the day and thus save candles. It was introduced in the U.K. in 1917 and then spread around the world.
Read more ....
What Perfumes Did Ancient Egyptians Use? Researchers Aim To Recreate 3,500-Year-Old Scent
 In X-rays, a liquid residue can be clearly seen in the ancient Egyptian perfume bottle. (Credit: Frank Luerweg, University of Bonn)
In X-rays, a liquid residue can be clearly seen in the ancient Egyptian perfume bottle. (Credit: Frank Luerweg, University of Bonn)From Science Daily:
ScienceDaily (Mar. 18, 2009) — The Ancient Egyptians cherished their fragrant scents, too, as perfume flacons from this period indicate. In its permanent exhibition, Bonn University's Egyptian Museum has a particularly well preserved example on display. Screening this 3,500-year-old flacon with a computer tomograph, scientists at the university detected the desiccated residues of a fluid, which they now want to submit to further analysis. They might even succeed in reconstructing this scent.
Pharaoh Hatshepsut was a power-conscious woman who assumed the reins of government in Egypt around the year 1479 B.C. In actual fact, she was only supposed to represent her step-son Thutmose III, who was three years old at the time, until he was old enough to take over.
Read more ....
The Science Of Spring

From Live Science:
The first day of spring is no guarantee of spring-like weather, but officially the season's start comes around at the same time each year nonetheless.
Well, sort of.
The first day of spring arrives on varying dates (from March 19-21) in different years for two reasons: Our year is not exactly an even number of days; and Earth's slightly noncircular orbit, plus the gravitational tug of the other planets, constantly changes our planet's orientation to the sun from year to year.
And weather-wise, Earth's seasons have shifted in the past 150 years or so, according to a study that came out last month. The hottest and coldest days of the years now are occurring almost two days earlier.
Read more ....
Wednesday, March 18, 2009
West Antarctic Ice Comes And Goes, Rapidly
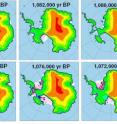 From E! SCience News:
From E! SCience News:Researchers today worry about the collapse of West Antarctic ice shelves and loss of the West Antarctic ice sheet, but little is known about the past movements of this ice. Now climatologists from Penn State and the University of Massachusetts have modeled the past 5 million years of the West Antarctic ice sheet and found the ice expanse changes rapidly and is most influenced by ocean temperatures near the continent. "We found that the West Antarctic ice sheet varied a lot, collapsed and regrew multiple times over that period," said David Pollard, senior scientist, Penn State's College of Earth and Mineral Sciences' Earth and Environmental Systems Institute. "The ice sheets in our model changed in ways that agree well with the data collected by the ANDRILL project."
Read more ....
Nobody Listens To The Real Climate Change Experts
From The Telegraph:
The minds of world leaders are firmly shut to anything but the fantasies of the scaremongers, says Christopher Booker.
Considering how the fear of global warming is inspiring the world's politicians to put forward the most costly and economically damaging package of measures ever imposed on mankind, it is obviously important that we can trust the basis on which all this is being proposed. Last week two international conferences addressed this issue and the contrast between them could not have been starker.
Read more ....
General Fusion Research Update

From The Next Big Future:
General Fusion is using the MTF (Magnetized Target Fusion) approach but with a new, patent pending and cost-effective compression system to collapse the plasma. They describe the injectors at the top and bottom of the above image in the new research paper. The goal is to build small fusion reactors that can produce around 100 megawatts of power. The company claims plants would cost around US$50 million, allowing them to generate electricity at about four cents per kilowatt hour.
If there are no funding delays, then in 2010-2011 for completion of the tests and work for an almost full scale version (2 meters instead of 3 meter diameter).
Read more ....
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




